INTRODUCTION
Here
I am going to demonstrate a real life example of Reverse engineering an
android application, there are basically two types of application frame work, one is purely based
on java another is a mixture of java and C or C++ Code. Here java is used as a
user interface and a wrapper to call processor intensive or security sensitive
code hidden behind shared library (.so files).
In this case I am not going to touch the java
section but will patch a shared lib file to remove licensing and limiting
features of the application to make it fully functional. The said application AirAudio has been randomly picked from Google
app store and is just used to demonstrate some reverse engineering techniques. I also strongly suggest anyone who intends to
regularly use this app to pay the required fees to legally use the App.
ABOUT REVERSE ENGINEERING
Reverse
engineering in the context of software is a process to understand the internal
working or say the logic of the compiled and optimized and most probably
obfuscated binary which is near impossible to directly understand by a
Programmer. Reverse Engineering in the ideal sense would be to recover complete
source code from the compiled binary then edit the source to make desired
changes and recompile the code to generate the binary with original
functionality but with changes desired by the programmer but in practical sense
it is rarely possible to go all the way nor desirable to achieve the required
the goal. The technique I applied here is to inspect the target compiled
library file narrowed down to just one or two Assembly instructions and
replaced with unconditional branch instructions to bypass a section of code.
ANATOMY OF AN ANDROID APP
It’s a format used to package and distribute android
application. An APK file contains all of that program’s code (such as .dex .so files),
resources, assets, certificates, and manifest file. Interesting thing is, It’s
just an archive file renamed with APK extension. To check, just rename it with
zip extension and extract it, you would get below the following files and
directories.
I used IDA Version 6.6 (32 bit) for
disassembly, HEX Editor NEO for Patching.
THE TARGET
AirAudio v6.2.1
is a very powerful audio streamer for Android and can Stream all audio even
system audio from any app to every receiver with just 1 click. This App
requires a rooted phone to hook or redirect system Audio.
THE HACKING
Download the target APK file here and use WinRar to
extract the contents of the APK file to a folder. With some hit and trial mixed
with experience and intuition I got down to the shared lib libbb.so this is the armeabi-v7a, there is also the x86 version
which is not covered. To start, fire up IDA the world’s best Disassembler, Click
File -> Open select libbb.so in \lib\armeabi-v7a\.
In the load new file dialog box select ELF for ARM if not auto selected keep
all other settings as it is and click OK Button. Decompilication will start and
will open up in a few seconds, in the Functions Window scroll down to find the Java_eu_airaudio_proxy_AudioProxy_transfer___3B
subroutine.
On
the right side of Functions Window there is the IDA View Window, select IDA
View-A Tab now scroll down a few hundred more lines to find the below text :-
This is the start of our
target Function but is not listed in the Functions Window, to list it in the
functions window click on the first assembly instruction -> .text:00005120 PUSH.W
{R4-R11,LR} Right click and
select Create Function
Now
you can see the function is listed in the Functions Window, this is our Target
function and we can remove the disabling feature which introduces annoying
audio BEEPS in the audio stream after 5 minutes of use. How I got down to the
exact location to patch is a different story and will probably require a
complete book on Reverse Engineering to explain every detail, for now, from the
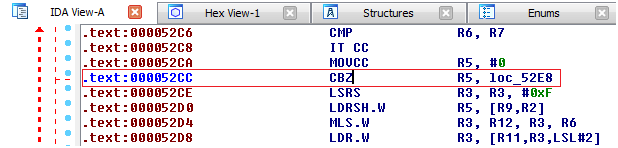
Jump Drop down Menu select Jump to Address. Enter Address 0x52CC in the Jump address edit box and click OK.
Now we see a conditional branch instruction
CBZ R5,loc_52E8
The annoying BEEP can
be disabled if I replace the conditional Branch to loc_52E8 with an
Unconditional Branch to loc_52E8, which means code execution will never reach
address 0x52CE and will always branch to loc_52E8 disabling the Audio BEEP.
Now the hex code
for original instruction CBZ R5,loc_52E8 is 0x65 0xB1, i need to replace this instruction with B loc_52E8 which is an unconditional branch to
loc_52E8. We know it is the assembler or compiler which
generates machine code from source code but here I will have to hand code the
replacement instruction and calculate the branch offset. According to the
documentation for the THUMB Instruction Set, the first 5 bits (11100b) decode
to an unconditional branch opcode, and the last 11 bits (00000001010b) decode
to Offset11, so the byte code for instruction B loc_52E8 translates to 0x0C 0xE0 to patch the lib file open the
file in a suitable HEX editor ( I used HEX
Editor NEO) Go to location 0x52CC and replace Hex bytes 65 B1 with 0C
E0 save the file and you are done.
Well this much takes care of the BEEPS but you will still
see the not licensed message when connecting to a receiver, so next I will
disable it to make it look as if it is licensed. On the functions window select sub_47EC
Replace the first instruction of the subroutine with BX LR this will effectively convert the subroutine into a
null sub which just returns without doing anything, which takes care of the
licensing part, with the file opened in the Hex Editor go to address 0x47EC and
replace Hex bytes 31 49 with 70 47 save the file to finish. Now we are done Patching and
will replace the original file with the patched file in the \lib\armeabi-v7a\
directory. Finally use Winrar to repackage the files into a Zip file, after the
Zip file is created change the extension from .zip to .apk and use signapk.jar
to sign the APK. Now you have an installable APK which is 100% functional.
hilogicsys@gmail.com